Describe Isotonic Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions
This causes water to rush into the cell. A cell placed into a hypotonic solution will swell and expand until it eventually burst through a process known as cytolysis.
Difference Between Isotonic Hypotonic And Hypertonic Definition Effect On Cells And Differences
These three examples of different solute concentrations provide an illustration of the spectrum of water movement based on solute concentration through the.

. Hypotonic solutions contain a lower concentration of solute compared to the cell. The opposite solution with a lower concentration is known as the hypotonic solutionScientists must describe cell contents compared to the environment. The cells stay the same.
An isotonic solution has a solute concentration equal to another solution. Hypertonic Solution Definition. Water relations and cell shape in blood.
INK VISUALL In the table below draw how each type of cell will look after being placed in a hypertonic solution. Appearance of Cells in a. Cells are in a hypotonic solution.
Hypertonic solutions are those in which more solute. Isotonic solutions where there is an equal concentration of solute in the cell and the solution are usually used in medicine. Hypotonic solutions are those with less solute again read as higher water potential.
The cells gain water. Join the thousands of other Critical Care Nurses that passed their CCRN exam after using our study tools study guides practice tests practice questions answers explanations and reports. Isotonic solutions have equal iso- concentrations of substances.
If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution the cell is considered. A hypotonic solution has a solute concentration lower than another solution. The cells lose water.
Cells are in a hypertonic solution. In hypotonic solutions there is a net movement of water from the solution into the body. Concentration of Solutions A hypertonic solution has a solute concentration higher than another solution.
A hypertonic solution contains a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution. Water potentials are thus equal although there will still be equal amounts of water movement in and out of the cell the net flow is zero. Cells are in an isotonic solution.
However some cases call for a.

Isotonic Vs Hypotonic Vs Hypertonic Solution Biology

Types Of Solutions Isotonic Hypertonic Hypotonic Animation Youtube
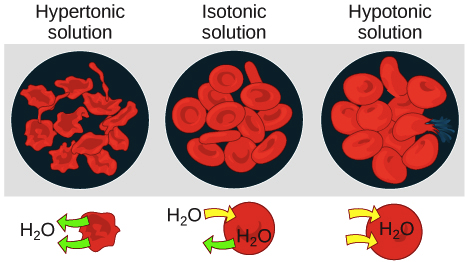
Tonicity Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Solutions Article Khan Academy
No comments for "Describe Isotonic Hypertonic and Hypotonic Solutions"
Post a Comment